Technical topics
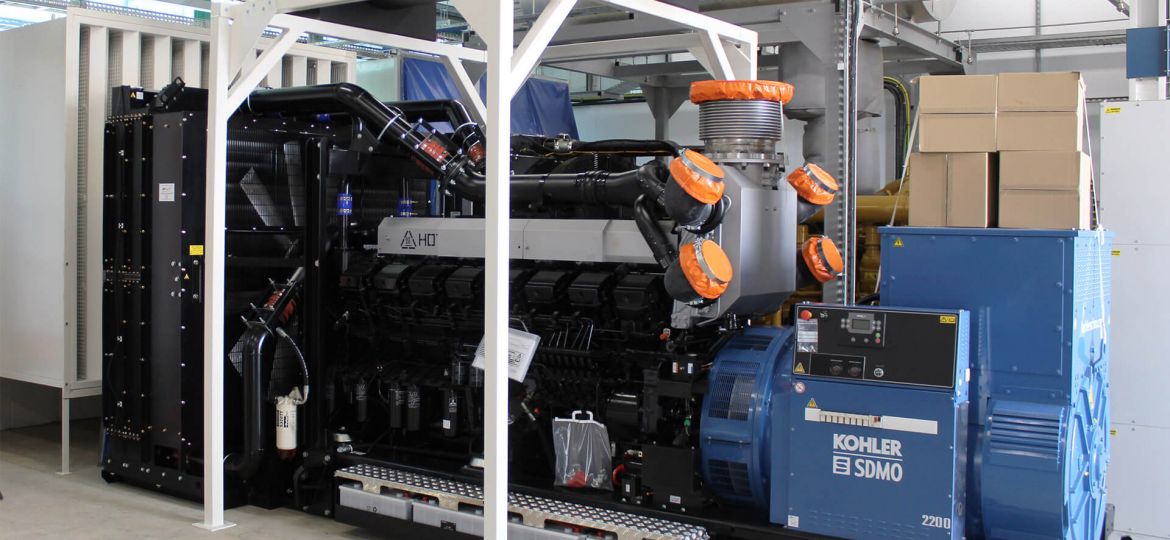
Protecting power generation equipment from damage due to abnormal conditions that exceed output ratings is paramount. The National Electric Code (NEC) mandates the coordination of protective devices in circuits powered by generators, especially for life safety loads. Utilizing voltage regulation controls to apply full excitation to the generator field during fault conditions can simplify coordination.
Designing and implementing a paralleling switchgear system can be complex due to the unique requirements of each power system. To address these challenges and reduce ambiguity during the design and operation phases, Kohler Power Systems has developed comprehensive sequence charts. These charts visualized in a step-by-step manner, document how a system will respond to both normal operations and system failures, ensuring no surprises during operation.
This post provides insights into digital communication systems used in electrical generating systems and emphasizes why answering these questions is critical. With this knowledge, stakeholders can develop comprehensive, well-thought-out specifications for the electrical generating system, avoiding pitfalls during installation and use.
In an era where clean energy is not just an option but a necessity, hydrogen stands out as a cornerstone in the quest for sustainable power generation. The leaps in technological advancements and shifts in regulatory landscapes have paved the way for hydrogen to become a focal point in discussions about the future of energy. This comprehensive article aims to demystify hydrogen technology, focusing on its application in internal combustion engines and fuel cells for electric power generation, tailored for the analytical minds of electrical engineers.
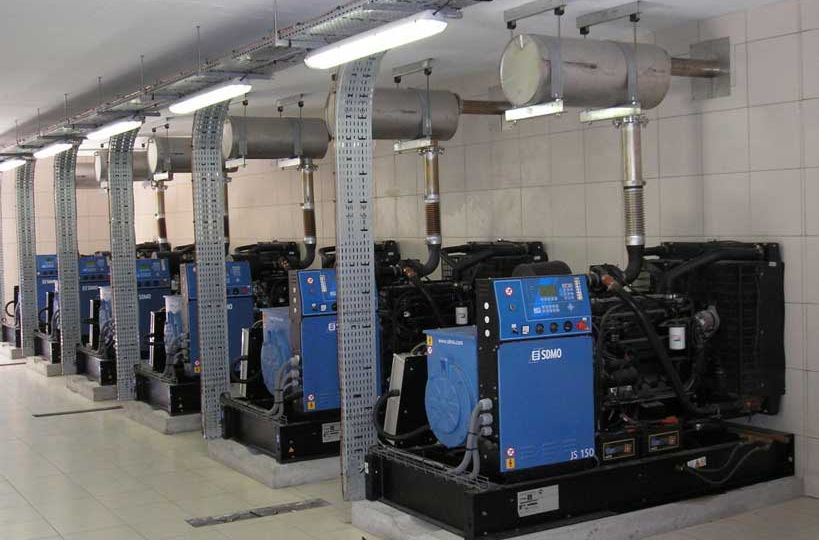
Optimizing the operational efficiency and reliability of power generation systems, the strategy of paralleling multiple generators surpasses the conventional reliance on a singular generator setup. This methodology not only introduces redundancy, bolstering both reliability and adaptability in power generation schemes but proves invaluable in scenarios demanding an uninterrupted power supply. The integration of multiple generators to the bus significantly augments the chances of sustained power amidst generator failures, a critical factor in life-safety applications.
This post is an in-depth exploration of the impact of motor starting loads on generator performance, a topic that is of utmost importance for the design of industrial and commercial applications (among many others) and that generally produces problems once the energy producing facilities are already in operation, for that reason the great usefulness of what we are going to analyze in this post.
For electrical engineers working with three-phase systems, it is common practice to postulate that loads will distribute evenly across the system coils, similar to what Figure 1 exemplifies. Yet, contrary to theoretical assumptions, real-life applications frequently present us with systems featuring unbalanced loads. One glaring example is the 120/240-volt three-phase delta system, frequently used for a mix of 120-volt and 240-volt single-phase loads as well as 240-volt three-phase loads. In essence, unbalance is the backbone of such systems, evidenced in instances such as a supermarket equipped with single-phase LED lighting and cash registers, and three-phase refrigeration and freezer motors.
Adding novelty to complex systems nowadays is the integration of motion-sensor-controlled lighting, which introduces another factor to consider in the balancing act of residual loads.