Generator safety is of utmost importance to ensure the well-being of individuals and the protection of property. Generators are essential devices that provide power when the main electrical grid is unavailable, but they can pose risks if not operated and maintained properly. In this article, we will discuss the necessary generator safety requirements and provide valuable insights to ensure a safe and efficient operation. It is important to note that these recommendations are valid for all types of generators, from an industrial scale generator to a portable generator for your home or camping.

The use of power generators comes with inherent risks that must be understood and mitigated following generator safety requirements to ensure the safety of both users and surrounding environments. Here is a list of main potential hazards that can involve it the bad use of generators:
- Fire hazard: Power generators produce heat and use flammable fuel, which increases the risk of fire if not properly operated or maintained. These fires can quickly spread and cause extensive damage.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning: Power generators emit carbon monoxide, a highly toxic gas, as a byproduct of combustion. If not used in a well-ventilated area or with proper exhaust systems, this gas can accumulate and cause severe poisoning or even death.
- Electrical shock: Power generators generate a considerable amount of electrical power, and improper use or faulty wiring can lead to electric shocks. This risk is heightened when users attempt to connect the generator directly to the electrical panel without professional assistance.
- Equipment failure: Power generators are complex machines, and any mechanical or electrical failure can lead to the generator not functioning properly or even completely breaking down. This can result in power outages, loss of productivity, and potential damage to connected devices or equipment.
- Fuel leakage: Improper handling or storage of fuel for power generators can lead to leaks, spills, or evaporation, creating fire hazards and environmental contamination. Fuel leaks can also damage the generator itself, leading to operational problems or failure.
- Improper grounding: Power generators require proper grounding to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
How to avoid the risks associated to generators use?
Placement and Ventilation
The placement of generators plays a crucial role in generator safety requirements, ensuring the safety of both the generator itself and the surrounding environment. When using a portable generator, it should be positioned outdoors, away from any structure, and in compliance with safety distance regulations. Additionally, considering weatherproof enclosures can provide added protection against harsh weather conditions and prevent unauthorized access or theft.
Indoor placement of generators should only be considered when absolutely necessary, and proper ventilation is essential in such cases. Adequate ventilation helps prevent the buildup of dangerous levels of carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas that can be lethal if inhaled in high concentrations. It is important to follow manufacturer guidelines and ensure proper airflow to minimize the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Additionally, precautions should be taken to prevent fire hazards, such as keeping flammable materials away from the generator and maintaining a clean and clutter-free environment.


Outdoor placement
1. Safety distance from buildings
The recommended safety distance from buildings for a power generator can vary depending on various factors such as the type and size of the generator, the fuel it uses, and local regulations. However, general guidelines suggest maintaining a minimum distance of 5 feet (1.5 meters) from any structures. This distance helps reduce the risk of fire hazards, including the potential for combustible materials near the generator to catch fire. It also allows for adequate ventilation and helps prevent carbon monoxide build-up within enclosed spaces.
2. Weatherproof enclosure options
There are weatherproof enclosure options available for power generators. These enclosures are designed to protect the generator from the elements, ensuring its safe operation in various weather conditions.
Weatherproof enclosures are typically made of durable materials such as steel or aluminum to provide strength and resistance against harsh weather conditions. They are designed to be solid and sturdy, protecting the generator from impacts and external damage.
Adequate ventilation is a crucial aspect of weatherproof enclosures to prevent overheating and ensure proper airflow for the generator. Enclosures often feature strategically placed vents or louvers that allow for sufficient air intake and exhaust, while also providing protection against rain and other precipitation.
Weatherproof enclosures must effectively seal against water ingress to safeguard the generator’s electrical components and prevent damage from moisture. This often involves utilizing gaskets and weather-stripping to create a watertight seal at access points, such as doors and cable entry points.
Some weatherproof enclosures also incorporate sound insulation materials or panels to minimize the noise generated by the running generator. This is particularly useful in residential or noise-sensitive areas where keeping noise levels to a minimum is essential.
3. Protection from theft and unauthorized access
Protecting your power generator from theft and unauthorized access is essential generator safety requirements to ensure its safety and availability when needed. Here are some measures you can take to enhance security:
- Install physical barriers: Erecting fences, barriers, or walls around your generator can deter unauthorized individuals from accessing it. Ensure that the barriers are sturdy, tall enough to discourage climbing, and have secure gates that are locked when not in use.
- Use security cameras and lighting: Install security cameras and motion sensor lighting near your generator to deter theft and monitor any suspicious activity. Visible cameras act as a deterrent, and well-lit areas discourage unauthorized access.
- Secure with locks and enclosures: Utilize sturdy locks to secure access doors and panels of the generator. Additionally, consider installing a weatherproof enclosure that has lockable doors and sturdy construction to prevent tampering or theft.
- Implement alarm systems: Install security alarm systems, such as motion detectors or sensors, to trigger alerts in case of unauthorized access to the generator. This can help deter thieves and notify you of any potential security breaches.
- Mark and register your generator: Engrave or mark your generator with a unique identification code or your contact information. This makes it easily identifiable and less enticing for thieves, as marked equipment is harder to resell. Additionally, register your generator with local authorities or organizations that track stolen equipment. This can aid in recovery efforts if it is stolen.
- Secure the fuel source: Store fuel for the generator in a secure, locked area away from the generator itself. Keep track of fuel levels and implement inventory control measures to ensure accountability and detect any fuel theft.
- Ensure adequate site security: Consider the overall security of the location where the generator is installed. Improve perimeter security with locks, security cameras, and good lighting. Restrict access to the generator by keeping surrounding gates or entry points locked.
- Educate and train staff: If the generator is located in a commercial or industrial setting, make sure employees are aware of the security measures in place and the importance of reporting any suspicious activity promptly.
Remember, it is essential to assess the specific security needs of your power generator and its location. Consider consulting with professionals who specialize in security systems and solutions to implement the most appropriate measures for your specific requirements.
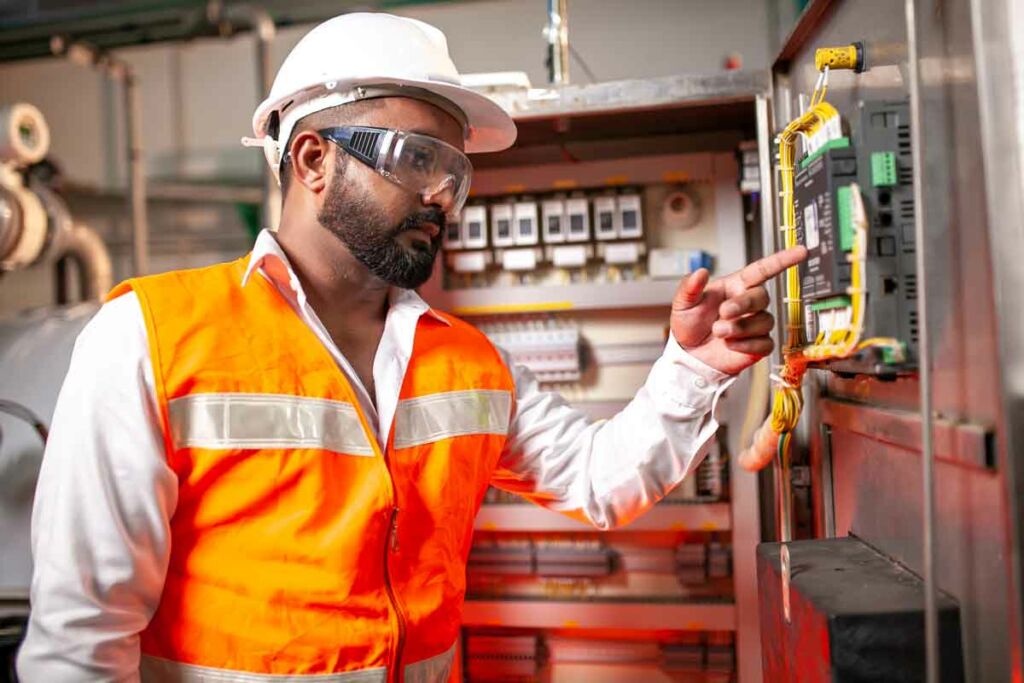

Indoor placement
1. Adequate ventilation requirements
Proper ventilation is crucial generator safety requirements for the safe operation when placed indoors. Inadequate ventilation can lead to a buildup of exhaust gases, such as carbon monoxide, which can be extremely hazardous. Here are some guidelines for adequate ventilation requirements for indoor placement:
- Ventilation area: Ensure that the generator is placed in a well-ventilated area. This means having sufficient space around the generator to allow for proper airflow. The recommended minimum space is typically at least three feet (one meter) on all sides.
- Air intake: The generator requires access to fresh air for combustion. Ensure that the location provides adequate air intake by ensuring that vents or openings are not blocked or obstructed. If necessary, install additional vents or ducts to ensure a constant supply of fresh air.
- Exhaust system: A proper exhaust system is essential in removing harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, from the indoor space. Install an appropriately sized and properly connected ventilation duct to direct exhaust fumes outside the building.
- Ventilation fans: Consider installing ventilation fans near the generator to assist with air movement. These fans can help maintain airflow and remove heat generated by the generator. Make sure the fans are properly sized, positioned, and vented to exhaust air outside the building.
- Natural ventilation: If possible, utilize natural ventilation options such as windows, doors, or skylights to provide additional airflow. These openings should be appropriately positioned to allow for cross-ventilation and the expulsion of exhaust gases.
- Monitoring systems: Install carbon monoxide detectors or other gas monitoring systems in the vicinity of the generator to provide early warnings in case of gas accumulation. These systems can alert you to any potential ventilation issues or gas leaks, ensuring prompt action can be taken.
- Compliance with local regulations: It is crucial to comply with local building codes and regulations regarding indoor generator placement and ventilation requirements. These regulations may vary depending on the generator’s size, type, and fuel source, as well as the specific building codes in your area.
Always consult the generator manufacturer’s guidelines and local authorities to ensure you meet the specific ventilation requirements for your generator model and location. Neglecting proper ventilation can result in health hazards, poor generator performance, and potential safety risks.
Carbon monoxide risks and prevention

To avoid carbon monoxide risks associated with power generators placed indoors, here are some recommendations:
1. Outdoor placement: The best way to eliminate carbon monoxide risks is by placing the power generator outside the building or in a well-ventilated outdoor area. This ensures that the exhaust gases dissipate and don’t accumulate indoors.
2. Proper ventilation: If placing the generator indoors is unavoidable, ensure the indoor space has proper ventilation. This includes opening windows and doors to allow for fresh air intake and exhaust. Create airflow by using fans or ventilation systems to help remove any buildup of exhaust gases.
3. Exhaust system extension: Install an exhaust system extension to direct the generator’s exhaust gases outside the building. This is typically a ventilation duct or pipe used to route the exhaust fumes away from the indoor space. Ensure the extension is correctly installed, properly sealed, and exits the building at a safe distance from doors, windows, or air intake areas.
4. Carbon monoxide detectors: Install carbon monoxide detectors near the generator and throughout the indoor space. These detectors should be placed at a height of about five feet (1.5 meters) above the floor and tested regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly. They will provide an early warning if carbon monoxide levels become hazardous.
5. Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your power generator, including inspections of the exhaust system, fuel lines, and ventilation components. Keep the generator clean and in good working condition to minimize the risk of gas leaks.
6. Education and warning signs: Ensure that everyone in the vicinity is aware of the potential dangers of carbon monoxide and the proper precautions to take. Display warning signs near the generator to remind people not to operate or refuel it indoors and to be cautious of the associated hazards.
7. Professional installation: If you are unsure about the proper installation and ventilation requirements for your power generator, consult a professional electrician or generator technician. They can assess your specific situation and provide guidance to minimize carbon monoxide risks.
Remember, carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas, making it extremely dangerous. Taking these precautions and regularly monitoring the indoor air quality can help prevent carbon monoxide poisoning and ensure the safe operation of your power generator.
SKU: A063B604
SKU: A063A442
SKU: A063A453
SKU: A063A449
Avoiding fire hazards
To avoid fire hazards associated with power generators installed indoors, consider the following recommendations:
1. Outdoor placement: Whenever possible, place the power generator outside the building or in a well-ventilated outdoor area. This greatly reduces the risk of fire hazards indoors.
2. Adequate clearance: If indoor placement is necessary, ensure that the generator is positioned in an area with sufficient clearance. Maintain a minimum distance of at least five feet (1.5 meters) between the generator and any flammable materials, such as furniture, curtains, or combustible storage. This helps prevent accidental ignition of nearby objects.
3. Fire-resistant enclosures: Install a fire-resistant enclosure specifically designed for power generators. These enclosures are constructed with materials that can resist high temperatures and help contain flames in case of a fire. Ensure the enclosure is properly installed and ventilated according to manufacturer guidelines.
4. Proper fuel storage: Store fuel for the generator in a separate, well-ventilated area away from the indoor generator placement. Choose appropriate containers specifically designed for fuel storage and follow safety guidelines for handling and storing flammable liquids.
5. Insulation and heat dissipation: Ensure that the generator and its electrical components are properly insulated and maintained to prevent overheating. Regularly check for any signs of wear or damage to wiring, connections, or insulation. Monitor the temperature of the generator during operation and ensure that it does not become excessively hot.
6. Fire extinguishers: Keep fire extinguishers readily available near the generator and in other areas prone to fire hazards. Ensure that they are regularly inspected, properly maintained, and easy to access. Train individuals in the vicinity on how to use the fire extinguishers effectively.
7. Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your power generator, including inspections of electrical components, fuel lines, and wiring. Proper maintenance helps detect and address any potential issues that could lead to a fire hazard.
8. Electrical safety: Ensure that the generator is correctly grounded and connected to an appropriate electrical system. Avoid overloading circuits and use surge protectors to prevent electrical malfunctions that can cause sparks or fires.
9. Education and awareness: Educate individuals who have access to the generator about fire safety precautions and emergency procedures. Display clear instructions and warning signs regarding the generator’s operation, proper fueling, and actions to take in case of a fire or emergency.
By following these recommendations, you can minimize the risk of fire hazards associated with power generators installed indoors, ensuring the safety of both the generator and the surrounding area.
Fuel Handling and Storage

Proper fuel choice
Gasoline vs. diesel vs. propane
Different fuels used by power generators (gasoline, diesel, propane) have varying safety considerations. Here’s a breakdown of the safety aspects associated with each fuel type:
Gasoline:
- Fire hazard: Gasoline is highly flammable, making it a significant fire risk. Proper storage of gasoline, away from ignition sources, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial to prevent accidents.
- Fuel stability: Gasoline has a shorter shelf life and can degrade over time, potentially causing operational issues if stale fuel is used. Regularly rotate and replenish fuel supplies to maintain fuel freshness and generator performance.
- Fuel spills: Gasoline spills can result in environmental contamination and fire hazards. Handle and store gasoline carefully, using approved containers and avoiding overfilling.
Diesel:
- Combustibility: Diesel fuel is less volatile compared to gasoline, reducing the risk of fire. However, it does still pose a fire hazard if mishandled or stored improperly.
- Fuel leaks: Diesel fuel leaks, if they occur, can lead to soil or groundwater contamination. Regularly inspect fuel lines, connections, and tanks for leaks, and address any issues promptly.
- Carbon monoxide emissions: Diesel generators still emit carbon monoxide gas, so proper ventilation and adherence to indoor placement guidelines are essential to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning risks.
Propane:
- Fire safety: Propane is highly flammable, and precautions must be taken to prevent fires. Propane tanks and connections should be properly maintained and inspected for leaks or damage.
- Storage and handling: Propane is stored under pressure, so proper storage and handling procedures are crucial. Propane tanks should be stored in well-ventilated areas, upright and secure, and away from ignition sources.
- Ventilation: When using propane indoors, proper ventilation is vital to prevent the buildup of potentially hazardous gases. Ensure that the indoor area has adequate airflow and that carbon monoxide detectors are installed and functional.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines specific to your generator and fuel type. Conduct regular inspections, maintenance, and fuel management practices to ensure the safe operation of your power generator. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local regulations and codes regarding the handling, storage, and use of the chosen fuel.
Fuel quality considerations
Fuel quality is a crucial generator safety requirements. Here are some key fuel quality considerations:
1. Fuel Contamination: Contaminated fuel can lead to engine malfunction, reduced performance, and potential safety hazards. Contaminants such as water, sediment, or microbial growth can adversely affect the generator’s operation. It is essential to store fuel in clean, sealed containers and regularly inspect it for signs of contamination.
2. Fuel Stability: Depending on the fuel type, stability can vary. Gasoline, for example, has a shorter shelf life and can degrade over time. Stale or degraded fuel can cause engine issues, reduced efficiency, and potential risks.
3. Fuel Quality Testing: Periodic fuel testing can help identify any potential contaminants or degradation. Professional fuel testing services can assess fuel quality, identify issues, and recommend appropriate treatments or fuel additives.
4. Proper Storage: Proper storage of fuel is crucial in maintaining fuel quality. Store fuel in appropriate containers, away from direct sunlight, and in well-ventilated areas. Follow manufacturer recommendations for maximum storage times.
5. Maintenance of Storage Tanks: If using large fuel storage tanks, regular maintenance is necessary. Tanks should be inspected for rust, corrosion, leaks, or any other damage that could compromise fuel quality.
6. Proper Filtration: Incorporating high-quality fuel filtration systems can help remove contaminants and ensure clean fuel delivery to the generator’s engine. Regularly inspect and clean or replace fuel filters as recommended by the manufacturer.
7. Fuel Additives: Depending on the fuel type and conditions, fuel additives may be recommended to enhance fuel stability, prevent degradation, or inhibit microbial growth. Consult with fuel experts or follow manufacturer recommendations for appropriate fuel additive usage.
8. Fuel Rotation: To prevent the use of stale fuel, practice fuel rotation by using the oldest fuel first and replenishing with fresh fuel. This helps ensure that fuel remains of good quality and minimizes the risks associated with degraded or contaminated fuel.
By maintaining fuel quality and following recommended fuel management practices, you can reduce the risks of engine malfunctions, poor performance, and potential safety hazards associated with the use of a power generator.
Electrical Connections and Grounding
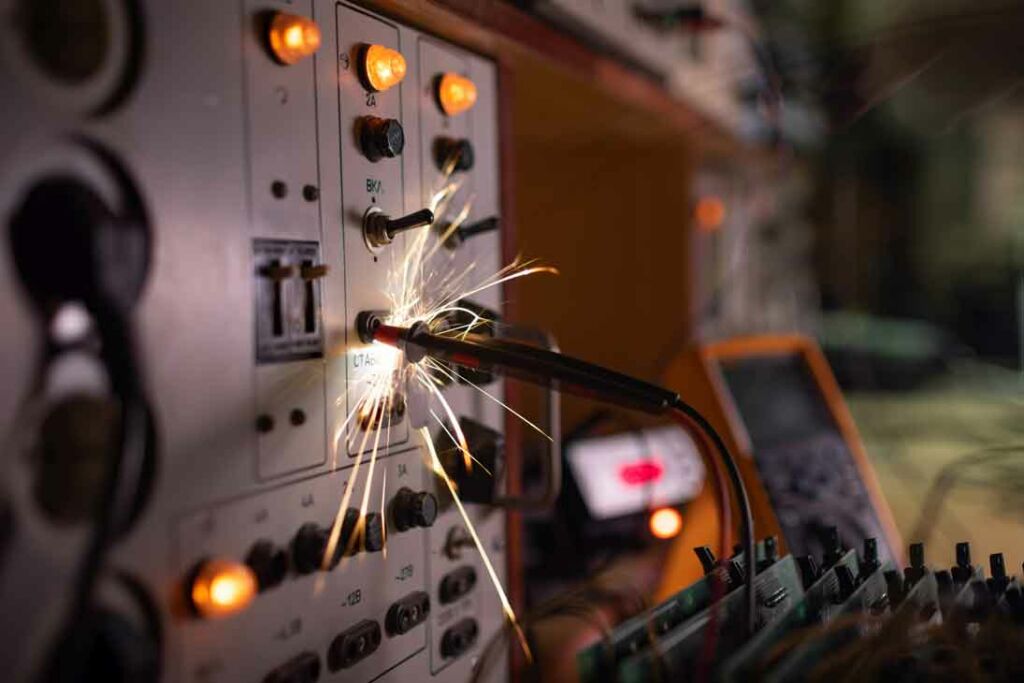
To ensure safety when using a power generator, proper electrical connections and grounding too are crucial generator safety requirements. Here are some recommendations:
1. Use a Transfer Switch: Install a transfer switch to connect the generator to your electrical system. This allows for safe and efficient operation by isolating your home’s wiring from the main power grid.
2. Size the Generator Correctly: Ensure that the generator’s capacity matches your power requirements. Oversized or undersized generators can lead to efficiency issues and potential safety hazards.
3. Use Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI): Install GFCI outlets or use GFCI adapters to protect against electric shock. GFCI devices continuously monitor electrical currents and quickly interrupt power if a fault is detected.
4. Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always refer to the generator manufacturer’s instructions on proper electrical connections and grounding. This will provide specific guidelines tailored to your generator model.
5. Proper Grounding: Follow the grounding instructions provided with your generator. Typically, grounding involves connecting a copper grounding electrode wire from the generator frame to a grounding rod or the main electrical system’s grounding point.
6. Avoid Backfeeding: Never connect the generator directly to your home’s electrical outlets or wiring without proper isolation through a transfer switch. Backfeeding can energize the power lines, posing a risk to utility workers and causing electrical hazards.
7. Use Heavy Duty Extension Cords: If using extension cords, ensure they are rated for the load and length needed. This will reduce the risk of overloading and overheating.
8. Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect all electrical connections and grounding to ensure they are secure and in good condition. Look for any signs of damage or wear, and address promptly if found.
9. Proper Ventilation: Generators emit exhaust gases, including carbon monoxide (CO), which is highly dangerous. Always operate generators in well-ventilated areas and ensure exhaust fumes are directed away from occupied spaces, doors, and windows.
10. Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of electrical connections or grounding for your generator, it is recommended to consult a licensed electrician or professional for guidance and assistance.
Remember, proper electrical connections and grounding not only ensure safety but also contribute to the reliable and efficient operation of your power generator.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Always follow the instructions provided by the generator manufacturer and consult a qualified electrician or professional for specific guidance relating to your equipment and electrical system.
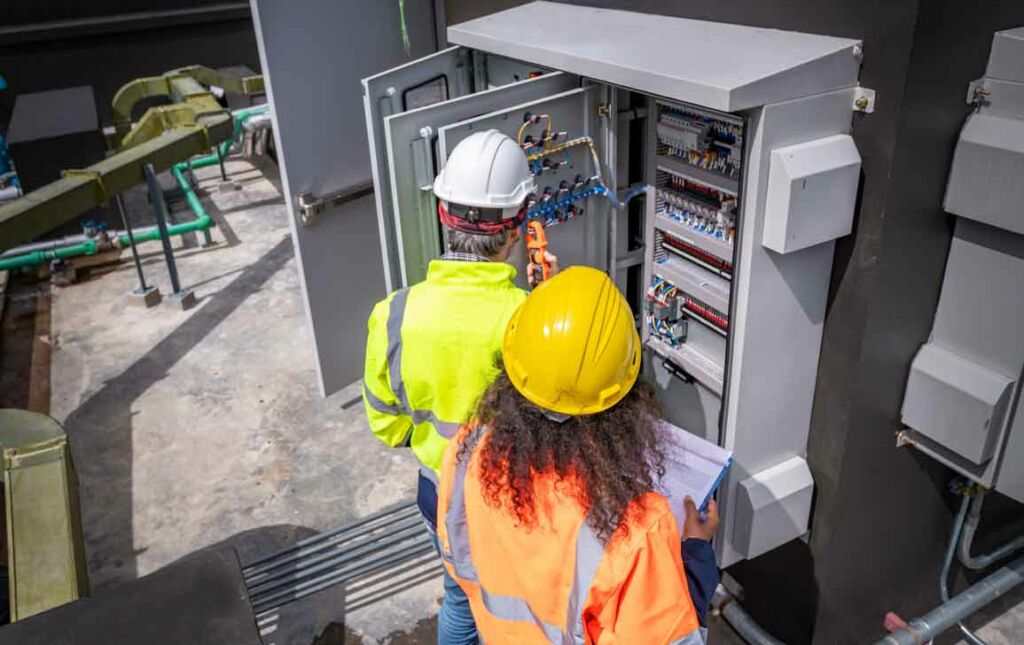

Generator safety requirements are crucial to ensure the safe and efficient operation of these essential devices. Whether using a portable generator for temporary power needs or a standby generator for continuous power supply, following proper guidelines and precautions is of utmost importance. This includes proper placement and ventilation, appropriate fuel handling and storage, safe electrical connections and grounding, and regular maintenance and inspections.
By adhering to these safety requirements, you can enjoy the benefits of generator power while minimizing the risks associated with improper operation. Remember, safety should always be the top priority when it comes to generators.
Don’t hesitate to reach out for any further information or assistance regarding generator safety requirements. Contact us at the phone number +1.954.657.7777, or write to us at info@bnhgenerators.com, and we will gladly help you.








