Now, in the 21st century, concern is increasing and widespread in relation to climate change and its catastrophic consequences for life on earth.
Climate change is no longer a distant and foreign news that happens somewhere unknown that does not affect us. Now climate change is present in our daily lives. It is a cause for concern for us and our loved ones and puts everything that is important in our lives at risk.
But what about climate change and diesel power generators? What is the impact on the environment of these important devices for our productive and family life? Here in this article we are going to help you understand this important current topic.


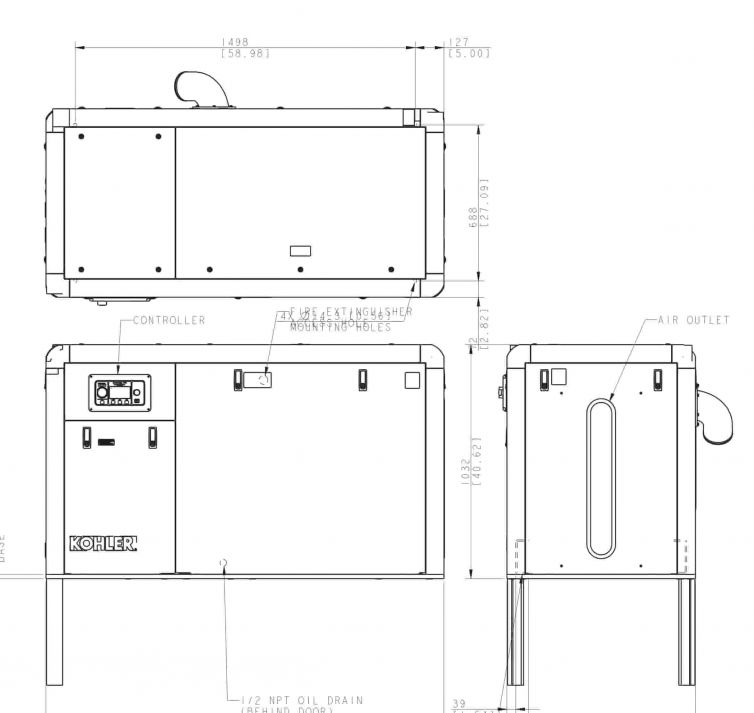
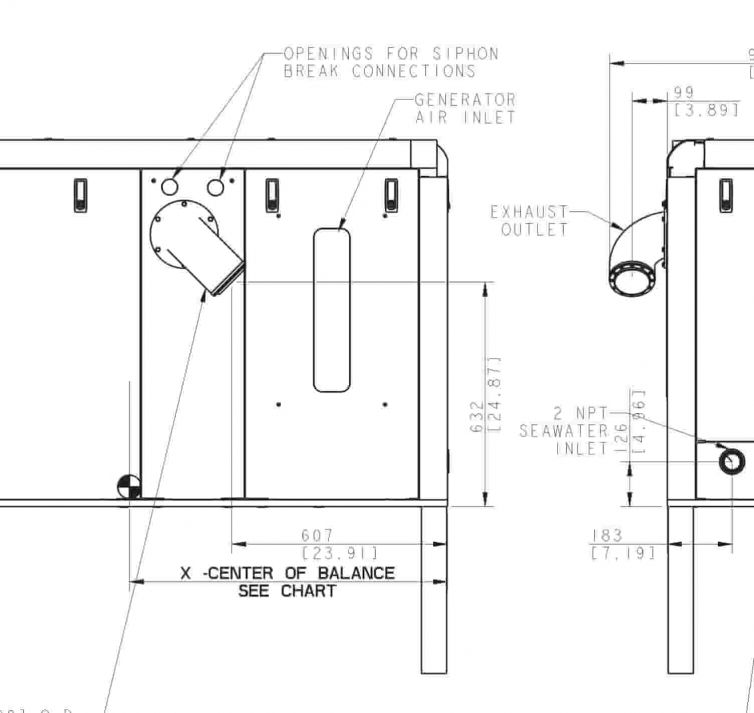
SKU: XM-D750UIV-A303_480


SKU: XM-D750UIV-A303


SKU: XM-D600UIV-A303_480


SKU: XM-D600UIV-A303
Understanding how a diesel generator works will help us understand which are the important factors to consider in order to reduce the carbon footprint that these useful and indispensable devices potentially can produce.
A diesel generator is the fusion that results from a diesel engine and an electric generator. The diesel engine is a high-performance thermal engine, which operates from the ignition of the fuel when injected with high pressure into an internal combustion chamber, and the electric generator is the device that will transform the movement generated by the diesel engine, which is mechanical energy, into electrical energy.
How do diesel power generators work?
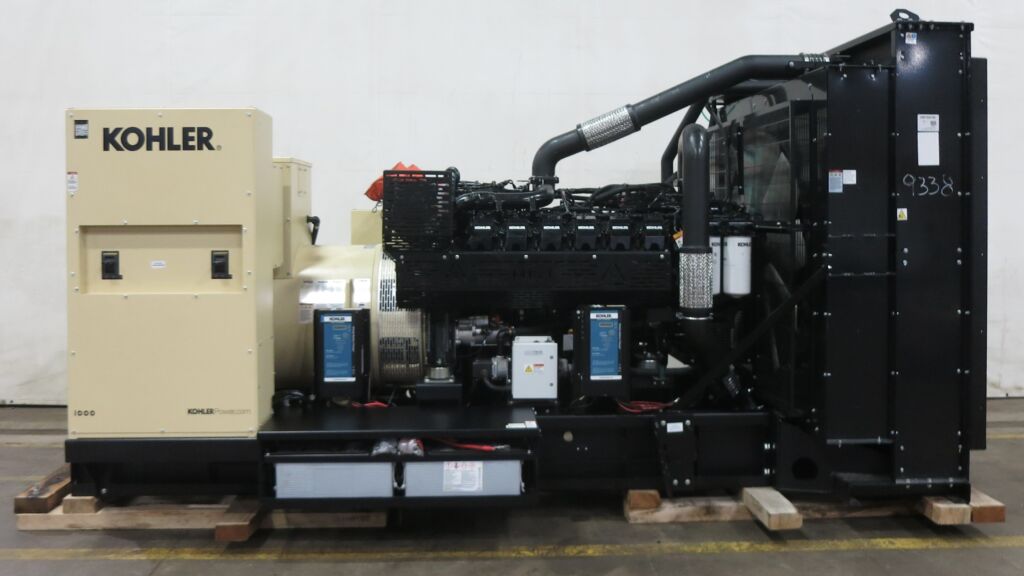

An electric generator works by transforming mechanical energy, such as that generated by an engine, into electrical energy.
The generator is able to drive the air from the environment into the interior to compress it. In turn, it injects the fuel, and the combination between the compression of the air and the injection of the fuel together with a spark in perfect synchrony, produces an intense heat, and this triggers the inflammation of the fuel that puts the generator’s shaft or core into rotation.
In turn, this movement generates electrical energy through a wire coil wrapped around the core.
The core is made of iron or some other type of magnetic material. When the core moves inside the coil, a magnetic field is generated that induces an electric current.
This current can be used to power a variety of electrical devices. The amount of electric current generated in an electric generator depends on several factors, such as the number of turns of the coil around the core, the size and speed with which the core moves, and the size of the coil. All these factors imply that the larger the energy we require, the larger the generator that produces it and the greater the fuel consumption is involved in the production of that energy.
Next we show a table, which allows us to have an approximate estimate, about the amount of fuel consumed by a generator, according to its size and the load.
| Generator Size (kW) | 1/4 Load (gal/hr) | 1/2 Load (gal/hr) | 3/4 Load (gal/hr) | Full Load (gal/hr) |
| 20 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.6 |
| 30 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 2.9 |
| 40 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 4 |
| 60 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 4.8 |
| 75 | 2.4 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 6.1 |
| 100 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 5.8 | 7.4 |
| 125 | 3.1 | 5 | 7.1 | 9.1 |
| 135 | 3.3 | 5.4 | 7.6 | 9.8 |
| 150 | 3.6 | 5.9 | 8.4 | 10.9 |
| 175 | 4.1 | 6.8 | 9.7 | 12.7 |
| 200 | 4.7 | 7.7 | 11 | 14.4 |
| 230 | 5.3 | 8.8 | 12.5 | 16.6 |
| 250 | 5.7 | 9.5 | 13.6 | 18 |
| 300 | 6.8 | 11.3 | 16.1 | 21.5 |
| 350 | 7.9 | 13.1 | 18.7 | 25.1 |
| 400 | 8.9 | 14.9 | 21.3 | 28.6 |
| 500 | 11 | 18.5 | 26.4 | 35.7 |
| 600 | 13.2 | 22 | 31.5 | 42.8 |
| 750 | 16.3 | 27.4 | 39.3 | 53.4 |
| 1000 | 21.6 | 36.4 | 52.1 | 71.1 |
| 1250 | 26.9 | 45.3 | 65 | 88.8 |
| 1500 | 32.2 | 54.3 | 77.8 | 106.5 |
| 1750 | 37.5 | 63.2 | 90.7 | 124.2 |
| 2000 | 42.8 | 72.2 | 103.5 | 141.9 |
| 2250 | 48.1 | 81.1 | 116.4 | 159.6 |
Once the electric current is generated, it can be stored in a battery to be used later (and not wasted) or used immediately to power electrical devices.
The electric current can be adjusted to adapt to the power required by the devices powered.
What are the benefits of diesel power generators?
- In areas where the climate is adverse and unpredictable, in remote areas or where the supply of electrical energy is very precarious or nil, diesel power generators can operate for prolonged periods without requiring periodic replenishment.
- Generators have become unit operations that allow industry to ensure business continuity, reduce costs or simply supply electrical energy to a variety of projects.
- Compared to other power generators, starting a diesel device will be much more economical and robust.
Do diesel power generators generate an environmental impact?
Currently, diesel generators represent an effective solution in most of our activities, since they are widely used in areas, applications and equipment that we could consider essential for our daily life.
We require them to supply electrical energy to production plants and industrial camps, hospitals, as backup power in business centers and apartment buildings. The list is endless, so we demonstrate that they are really necessary for the effective operation of the productive devices of commercial and domestic life.
Although it is true that diesel generators represent an effective solution in most of our activities, these trigger a harmful impact on our environment if they are not installed, used and maintained correctly.
Here we talk about the fact that the combustion of diesel produces what we know as greenhouse gases, that is, gases that absorb and accumulate CO2 (carbon dioxide), methane, nitrogen oxide, in addition to pollutant particles such as lead and benzene, among others, when the diesel combustion does not occur effectively.
Disadvantages of a diesel generator related to the type of installation, use and maintenance:
- Despite its robustness, diesel generators need preventive and frequent maintenance to guarantee their safe and effective operation. This implies the use of adequate lubricants and filter changes, fuel with special additives to optimize and purify the combustion of our generator, and that reduce the rate of pollutant emissions.
- When an incomplete diesel combustion occurs, or the recommended additives are not used, the device can generate emissions of gases that damage the ozone layer.
However, The manufacturers are solving this problems by implementing new technologies of:
- Direct injection.
- Hybrid fuel systems.
- Emission control.
- Exhaust gas recirculation systems using diesel catalysts and filters, which cool the combustion and reduce emissions.
Other new energy generation technologies in diesel generators.
Engine manufacturer Kohler Engines has approved the use of EN15940-compliant hydrotreated vegetable oils (HVOs) for all its diesel engines – either pure or as a blend with conventional diesel.
Laboratory and field testing have confirmed that Kohler diesel engines require no modification to use HVO. However, use of exhaust gas after-treatment systems will still be necessary where already required.
Pure or blended, it can be used in any Kohler engine, whether liquid-cooled from the KDI and KDW lines or air-cooled from the KD line, the company said. In addition, no variations to the maintenance schedule are required and normal European warranty conditions apply.
HVO is a renewable paraffinic fuel also known as synthetic diesel. It is produced with plant or animal oils derived from the residues of the meat and fish industries. Since it is obtained from organic material, HVO – unlike biodiesel – does not use agricultural resources or contribute to deforestation.. A reduction in overall CO2 emissions of up to 90% can be obtained depending on the raw material employed in HVO production.

Kohler has implemented in its diesel generators the HVO or Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil system, which is a fuel made from vegetable oils, completely biodegradable.
These oils are a combination of alkanes and ethoxylated oils (oils whose organic compounds are subjected to an oxidation process that replaces hydrogen atoms with oxygen atoms, producing less polluting and more stable and lightweight molecules), which results in a totally renewable fuel, without sulfur and with a minimum rate of greenhouse gas emissions.
All Kohler diesel generators, new or already installed, are fully compatible with HVO, with more refined engines, more efficient, and whose systems are aligned to reduce emissions.
This means that if our customers decide to minimize their carbon footprint, they can use their diesel generators without the need to adapt another complementary device.
HVO is analogous to fossil diesel, in such a way that it can be added to the tank directly or used as the only source of fuel, and does not require different maintenance from the usual.
HVO fuel has a lower density, meaning that the mass of fuel injected per cycle is lower than that of EN590 diesel, reducing power and torque performance by 1 and 5%. This effect is partly compensated by a higher cetane number (75 for HVO compare to 51 for EN590 diesel), which translates into positive effects on combustion.
If you have any questions about what we have commented on in this article or require support, do not hesitate to contact our customer support team.
At Brags & Hayes we offer you all the necessary support to advise you on the purchase of this wonderful and necessary source of alternative energy, to equip your home, business or factory.
Contact us at the phone number +1.954.657.7777, or write to us at info@bnhgenerators.com, and we will gladly help you.
SKU: 32EKOZD-CP1_24VDC
SKU: 80EOZD-CP1-3PH_208
SKU: 125EFOZCJ-CP1-3PH_400
SKU: 7EFKOZD-CP1
SKU: 28EFKOZD-CP1_Open
SKU: 70EFOZDJ-CP1-3PH_400
SKU: 150EOZDJ-CP1-3PH_208
SKU: 9EFKOZD-CP1