When selecting or installing a generator, understanding its rating is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and durability. This guide delves into the procedures and standards outlined in a technical document for determining generator set ratings, focusing on practical applications for technicians and users.
Generator ratings define the operational limits and performance characteristics of a generator under specific conditions. They include parameters such as load factor, operational hours, and overload capabilities. These ratings help in selecting the right generator for standby, prime, continuous, or marine applications.

Key Rating Categories
Standby Rating
- Designed for emergency power during outages.
- Operates at variable loads with a load factor of less than 85%.
- Limited to 400 hours per year.
- No overload capability.
Prime Rating
- Used as the primary power source for sites without utility power.
- Handles variable loads with a load factor below 75%.
- Allows for unlimited operating hours and a 10% overload for 1 hour in 12.
Limited Running Time
- Continuous use under a constant load for up to 700 hours annually.
- No overload capability.
Base Load Rating
- Operates continuously under a constant load without time limitations.
- No overload capabilities, but ensures high durability with a typical overhaul time exceeding 20,000 hours.
Marine Continuous Rating
- Designed for marine applications, including pleasure and commercial craft.
- Operates with a load factor of less than 75%.
- Usage varies: under 400 hours annually for pleasure craft and 2,000 hours for commercial craft.
How Are Generator Ratings Calculated?
The calculation involves understanding the power output of the generator’s engine and alternator efficiency. Here’s the process:
Base Equation
Generator Set Output (kW)=[Engine Output (HP)−Parasitic Loads (HP)]×Alternator Efficiency×0.746
- Parasitic loads include components such as cooling fans, air intake, and exhaust restrictions.
- Excludes battery charging alternators.
Adjustments for Standard Conditions
- Observed outputs are corrected using formulas considering temperature, barometric pressure, and alternator efficiency. Reference conditions are standardized at 77°F (25°C) and 29.2 in. Hg (99 kPa).
Production Testing
- During production tests, measured output is allowed a 5% variation for engine differences and adjustments for engine run-in phases.
Special Considerations for Alternators
Alternator ratings play a significant role in defining the generator’s capabilities:
Temperature Rise Limits
Alternators must adhere to specified temperature rise limits, determined by insulation class (F or H). For instance, standby alternators can have a higher temperature rise than continuous-duty alternators.Efficiency Testing
Efficiency curves for alternators are determined through dynamometer testing, following IEEE standards. These curves highlight performance across various load ranges.
Marine, Mobile, and Custom Ratings
Different applications impose unique requirements on generators.
Generators designed for marine, mobile, and other specialized applications must meet unique operational demands and regulatory standards. These environments often present challenges such as extreme temperatures, limited space, variable loads, and regulatory compliance, all of which influence the design, rating, and performance of the generator set. Below is an in-depth exploration of these specialized ratings and their practical implications.
Marine Ratings: Generators for the Open Sea
Marine environments demand robust and reliable power generation systems, especially given the harsh conditions and strict safety requirements. Marine generator ratings reflect these needs, incorporating design and operational considerations for both pleasure and commercial vessels.
Environmental Factors and Temperature Rise Limits
Marine generators are often exposed to higher ambient temperatures, sometimes exceeding 50°C (122°F), due to confined spaces, engine rooms, and reduced ventilation aboard ships. To ensure reliability:- Generators are rated for temperature rises in line with NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) standards.
- Insulation Classes F and H are commonly used, with maximum temperature rises of 120°C for Class F and 140°C for Class H insulation. These limits ensure durability despite high ambient temperatures.
Load Variability and Duty Cycle
- Pleasure Craft: Typically used for recreational purposes, these generators operate for fewer than 400 hours per year and face variable load demands. Efficiency and noise reduction are prioritized.
- Commercial Craft: For vessels such as fishing boats and transport ships, generators are rated for up to 2,000 operational hours annually. They must handle more demanding, continuous loads and higher power outputs.
Regulatory Compliance
Marine generators must comply with Coast Guard regulations (46 CFR, Chapter 1), which enforce standards for safety, insulation, and temperature rise limits. Compliance ensures that generators are both safe and reliable for marine use.Special Features for Marine Generators
- Corrosion Resistance: Materials used in marine generators are often treated or constructed to resist saltwater corrosion.
- Compact Design: Limited space aboard ships requires compact, high-power-density generators.
- Vibration and Shock Tolerance: Marine environments expose generators to continuous vibrations and occasional shocks, requiring rugged designs.
Mobile Ratings: Generators for On-the-Go Power

Mobile generators cater to applications such as recreational vehicles (RVs), trailers, and portable power solutions. These generators must balance portability, efficiency, and adherence to specific safety standards.
Operational Standards
Mobile generators are rated under UL 1248 (Engine Generator Assemblies for Use in Recreational Vehicles). Key specifications include:- Temperature rise limits of 120°C for Class F insulation and 140°C for Class H insulation.
- Ratings designed for intermittent, varying loads rather than continuous use.
Design Considerations
- Lightweight and Compact: For RVs and mobile units, the generator must fit within limited storage spaces and be easy to transport.
- Noise Reduction: Mobile environments prioritize quieter operations, often incorporating advanced mufflers and vibration isolation systems.
- Fuel Efficiency: Mobile generators often run on gasoline, diesel, or propane, with designs optimized for lower fuel consumption to extend operation time between refueling.
Environmental Adaptability
Mobile generators must withstand diverse environmental conditions, from extreme heat to sub-freezing temperatures, making robust construction essential.
Custom Ratings: Tailoring Generators for Unique Needs

In some cases, standard generator ratings are insufficient for meeting specific operational or environmental requirements. Custom-rated generators are designed to bridge this gap, addressing unique challenges through tailored specifications.
Adjustments for Environmental Conditions
- High Altitudes: Air density decreases with altitude, reducing engine performance. Generators for high-altitude applications are derated to account for reduced oxygen availability. For example, naturally aspirated engines might lose 3% power for every 1,000 feet above sea level.
- Extreme Temperatures: In hot climates, additional derates are applied. For example, naturally aspirated engines often lose 1.5% power for every 9°F (5°C) increase above the standard 77°F (25°C).
Application-Specific Modifications
- Industrial Generators: Custom ratings for industrial applications might include oversized cooling systems or alternators for enhanced performance under continuous, high-load conditions.
- Offshore Generators: Designed for oil rigs and offshore platforms, these generators feature explosion-proof enclosures and corrosion-resistant materials to handle salt spray and potential hazardous environments.
Compliance with Unique Standards
Custom generators often need to comply with additional standards beyond typical NEMA or IEEE requirements. For instance, offshore generators may need certifications from entities such as ABS (American Bureau of Shipping) or DNV (Det Norske Veritas).Specialized Features
- Remote Monitoring: Advanced telemetry systems allow operators to monitor generator performance remotely, essential for isolated installations.
- Redundancy: Custom systems for critical applications often include redundant components to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Comparison of Marine, Mobile, and Custom Ratings
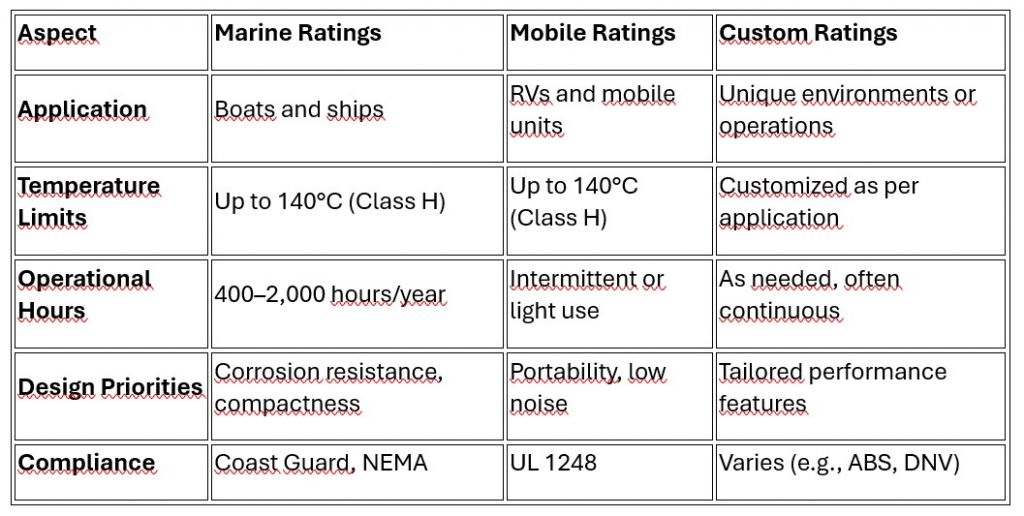
Practical Implications for Users and Technicians
Sizing the Generator Appropriately
Match the generator’s rating to the intended application. For instance, a standby-rated generator might fail if used continuously, leading to overheating and reduced lifespan.Considering Overload Needs
For applications with peak load demands, prime-rated generators are ideal as they allow temporary overload.Accounting for Environmental Conditions
Temperature and altitude significantly impact generator performance. Adjustments or derates are necessary to ensure reliable operation in extreme conditions.Maintenance and Durability
Understanding the overhaul intervals associated with different ratings helps in planning maintenance schedules and estimating operational costs.
Generator Set Performance Optimization
Beyond rating calculations, ensure optimal performance by focusing on these factors:
- Testing Under Real-World Conditions: Simulate operational loads to verify that the generator performs as expected.
- Regular Inspections: Check for parasitic load changes, which might alter efficiency.
- System Integration: Ensure that all components, from alternators to cooling systems, are compatible and tuned for the application.
Generator ratings are more than just numbers; they represent the foundation for reliable and efficient power generation. By understanding these ratings and applying the calculation and correction methods, technicians and users can ensure that their power systems meet both immediate and long-term demands.
With proper sizing, testing, and maintenance, generators can provide seamless and dependable service in any application, from emergency backup to continuous power for critical operations.


